Tutorial 2: Simple Mineral Prospectivity Maps with Kalpa#
Tutorial by
Utpal Singh¹, Satyam Pratap Singh¹, Sourabh Motiani²
¹ School of Geosciences, University of Sydney
² Department of Earth Sciences, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee
In this tutorial, we will use Kalpa to build a mineral prospectivity map. The process utilizes three types of datasets:
Geophysical data (e.g., Bouguer Gravity Anomaly, Magnetic Anomaly)
Geological data (e.g., geological age, folds, faults, lineaments)
Satellite data (e.g., ASTER, SRTM, and LANDSAT)
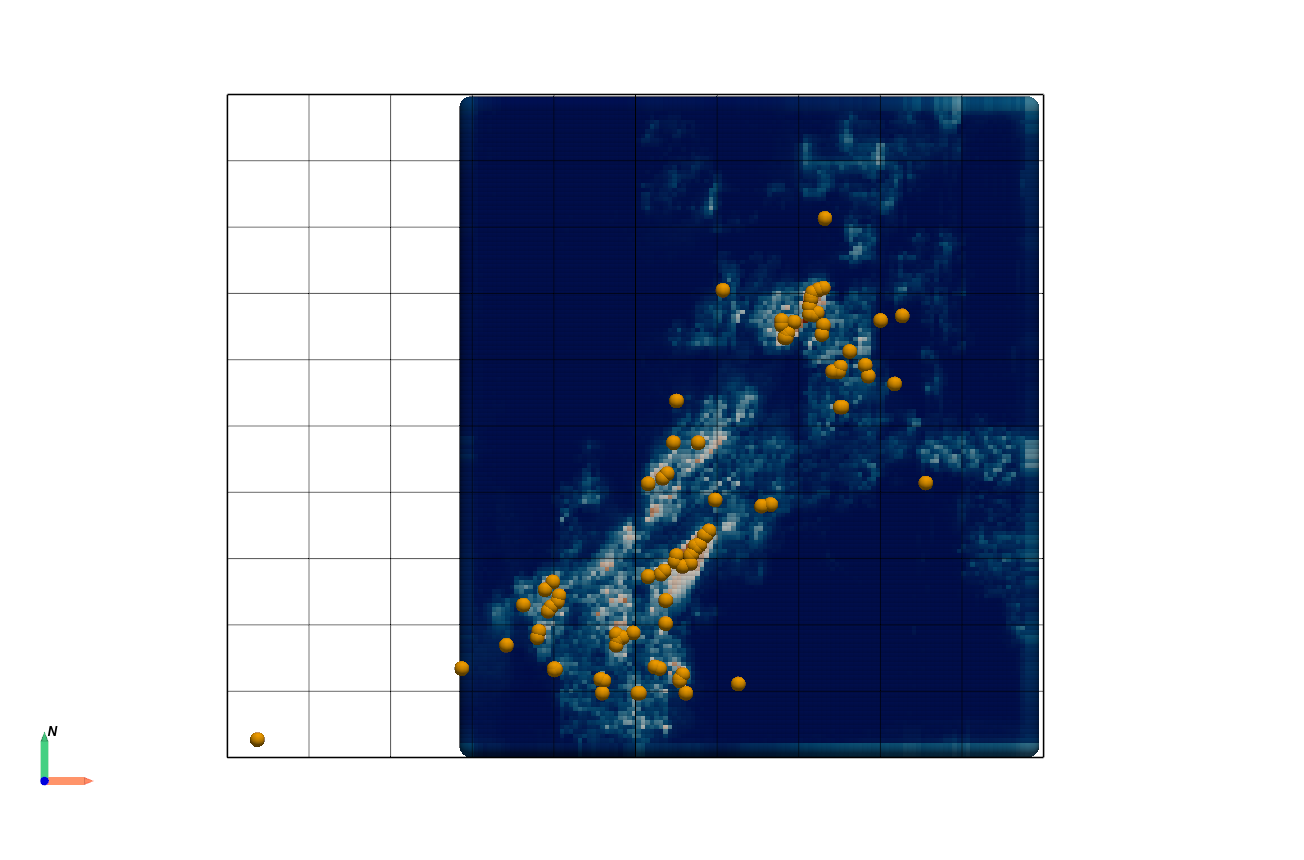
The goal is to create prospectivity maps for copper deposits based on the known occurrences of 96 mineral deposits in the study region.
We will sample various datasets at the locations of known copper occurrences, create an unlabeled dataset for contrast, and use Random Forest (RF) classifier and regressor to label and map prospectivity.
Dataset Overview#
The dataset can be downloaded here.
Geophysical Data#
Gravity Data:
Observed Gravity
Theoretical Gravity
Bouguer Anomaly
Upward Continued Bouguer Anomaly
Directional Derivatives of Bouguer Anomaly
Magnetic Data:
Observed Magnetism
IGRF
Magnetic Anomaly
Upward Continued Magnetic Anomaly
Directional Derivatives of Magnetic Anomaly
Geological Data#
Tectonic Age
Folds
Faults
Lineaments
Satellite Data#
LANDSAT8 Bands:
Multispectral bands (1 to 9) as NetCDF files
SRTM Elevation Data:
Elevation values from the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM)
ASTER Data:
Multispectral bands (1 to 14) as NetCDF files
Mineral Occurrences:
The dataset includes 96 known occurrences of mineral deposits. For this tutorial, we focus on copper deposits.
Workflow#
Step 1: Loading Data and Visualization#
Start Kalpa and create a new folder named
MineralProspectivityto save the dataset, figures, etc.
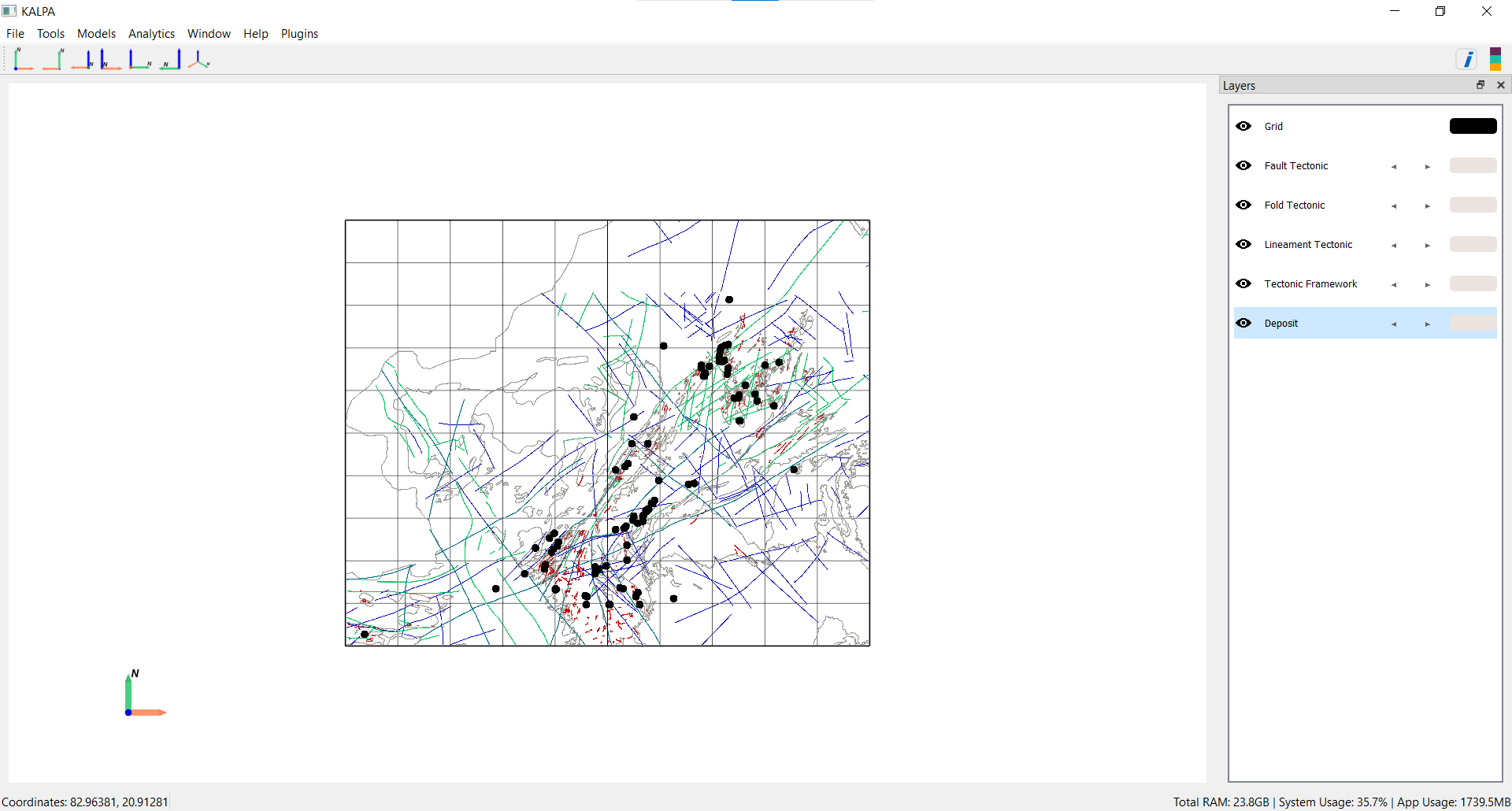
Import Vector Data:
Navigate to File > Import > Vector Data.
Load the following files:
ShapeFiles/Fault_Tectonic.shpShapeFiles/Fold_Tectonic.shpShapeFiles/Lineament_Tectonic.shpShapeFiles/Tectonic_Framework.shpDeposits/Deposits.shp
Adjust colormap, feature width, and range as needed.
Import Raster Data:
Navigate to File > Import > Raster Data.
Load the following files:
GeophysicalProcessed/Raster/BOUGUER_AN_Kriging.ncGeophysicalProcessed/Raster/MAGNETIC_A_Kriging.ncGeophysicalProcessed/Raster/Grad_Gravity/*GeophysicalProcessed/Raster/Grad_Magnetic/*GeophysicalProcessed/Raster/UC_Gravity/*GeophysicalProcessed/Raster/UC_Magnetic/*SatelliteData/SRTM/SRTM_Raj_India.ncSatelliteData/LANDSAT/Band_1_LANDSAT.nctoBand_9_LANDSAT.nc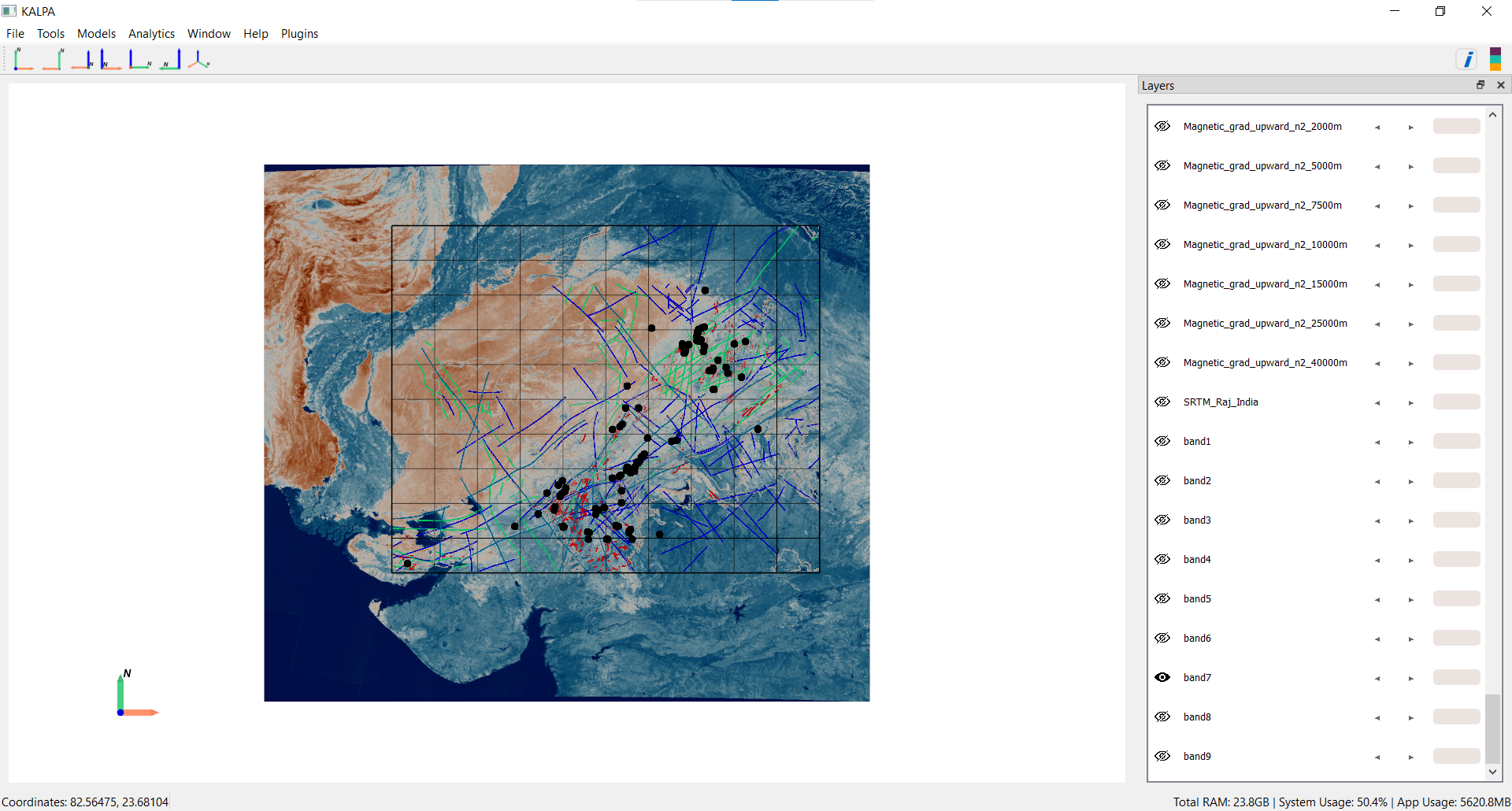
Step 2: Feature Generation#
Generate Positive Labels from Known Deposits:
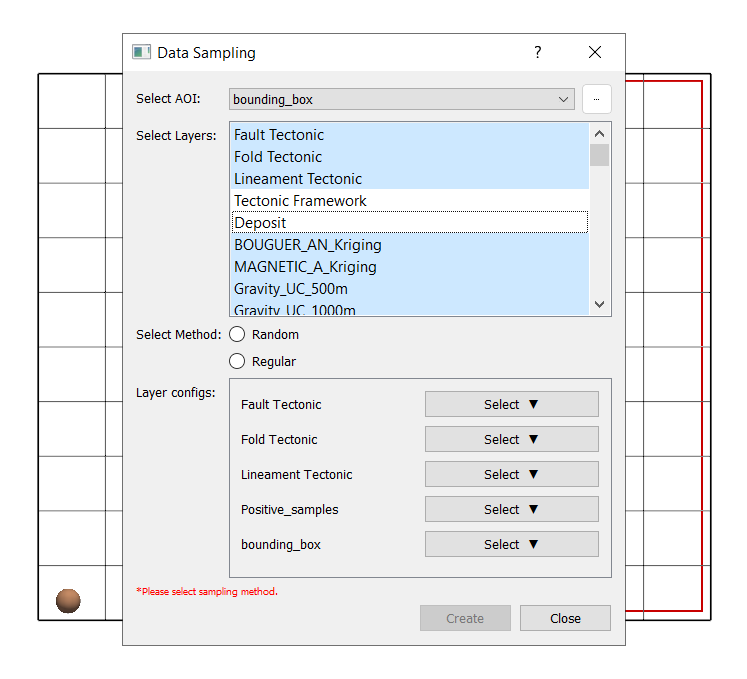
Navigate to Tools → Data Sampling.
AOI (Area of Interest): Deposit.
Select all layers except Tectonic Framework and Deposit.
Layer Configuration:
Select the columns to be sampled for vectors having multiple columns:
Fault_Tectonic
Fold_Tectonic
Lineament_Tectonic
For rasters, select Band Value in case of multiple bands.
Sampling method: Random with default seed points as number of deposits are less than default value in this case.
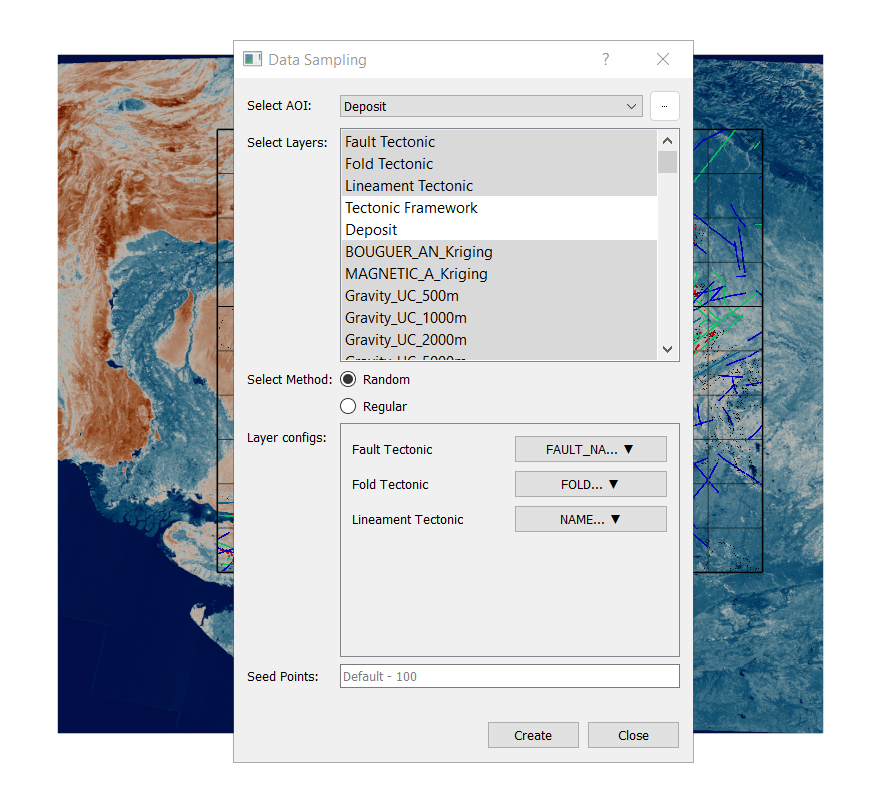
Click Create → Save as:
Positive_samples.gpkg.
Create Bounding Box:
Navigate to Tools → Vector → Bounding Box.
Select layer:
BOUGUER_AN_Kriging
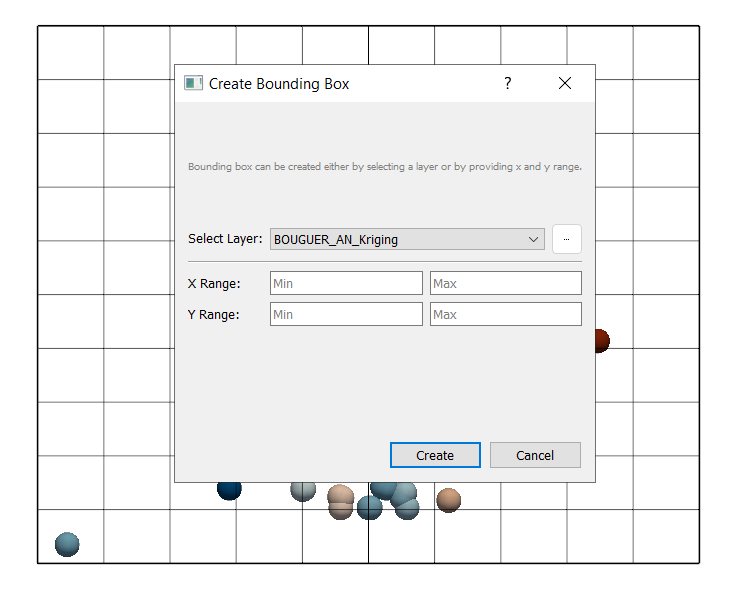
Click Create → Save as:
bounding_box.gpkg.
Generate Unlabelled Features:
AOI: bounding_box.
Select all layers except Tectonic Framework, Deposit, bounding_box, Positive_samples.
Method: Random, 3000 seed points.
Layer Config:
Select the columns to be sampled for vectors having multiple columns:
Fault_Tectonic
Fold_Tectonic
Lineament_Tectonic
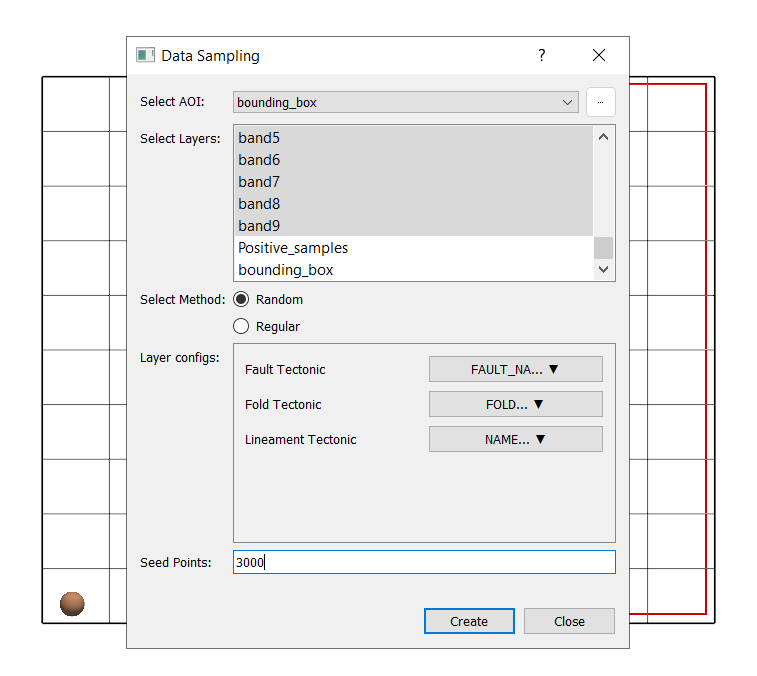
Click Create.
Save as:
Unlabelled_samples.gpkg
Generate Label Column:
Navigate to Tools → Vector → Calculator.
Layer: Positive_samples.
Condition: ‘1’ for positive samples.
Column name: Label.
Click Apply.
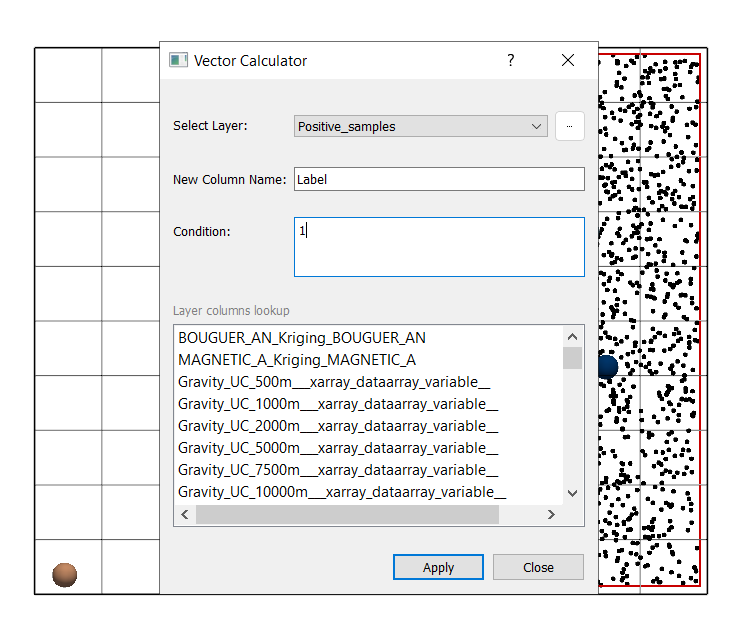
Save as:
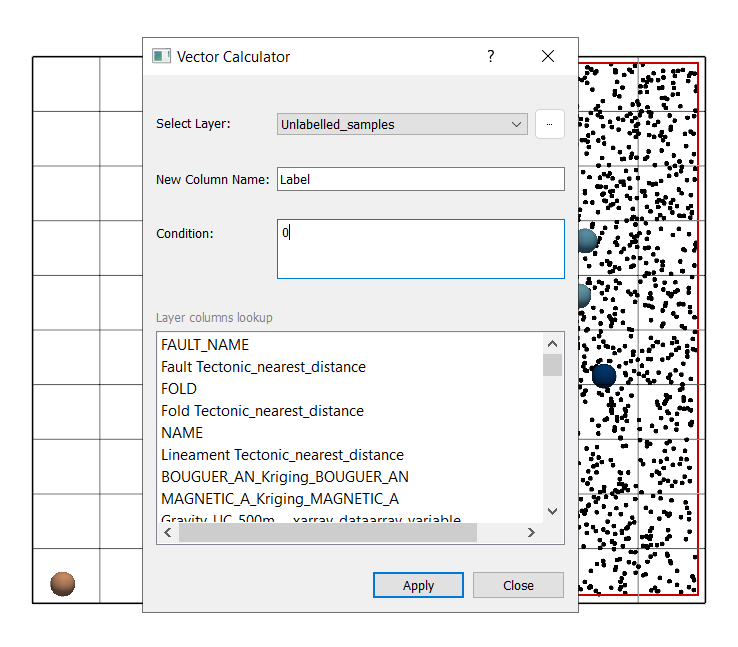
Positive_Label_calculated.gpkgRepeat the same steps for Unlabelled_samples with condition ‘0’.
Save as:
Negative_Label_calculated.gpkg
Merge Positive and Unlabelled Datasets:
Navigate to Tools → Vector → Merge Layers.
Layers: Positive_Label_calculated.gpkg and Negative_Label_calculated.gpkg.
Merge direction: Row Wise.
Click Merge.
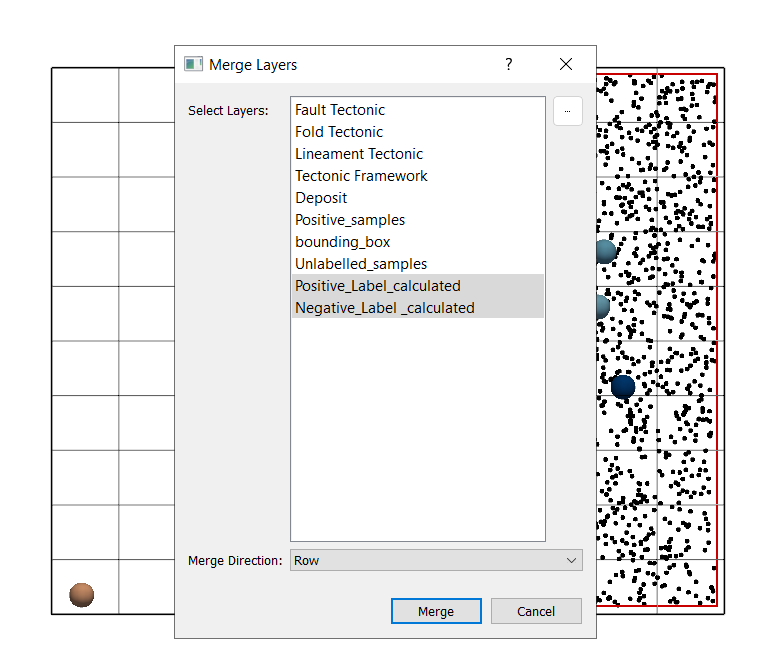
Save as:
Training_Dataset.gpkg
Step 3: Create PU Bagging Model#
Navigate to Models → Supervised → PU Bagging.
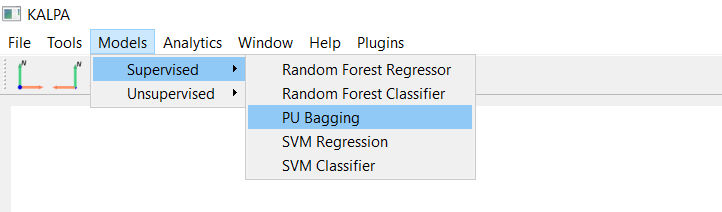
Select Create New Model.
Training data:
Training_Dataset.gpkg.(Optional) Generate correlation report to examine feature correlation.
Target feature: Label.
Select all other features as training features (except Label).
Tune other hyperparameters as needed.
Enable: scaled probabilities.
Click Start Training.
Save model as:
PU_Model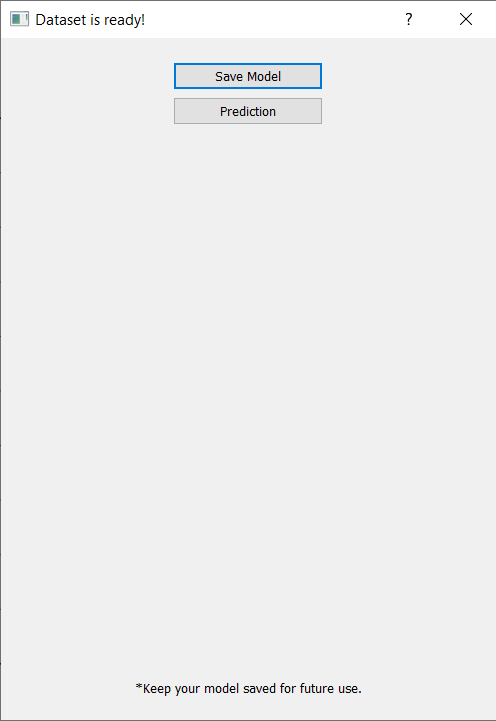
Step 4: Prediction and Visualization#
Extracting Regular Grid for Prediction:
Navigate to Tools → Data Sampling.
AOI: bounding_box.
Select all layers except:
Tectonic Framework
Deposit
Positive_samples
Unlabelled_samples
bounding_box
Training_Dataset
Positive_Label_calculated
Negative_Label_calculated
Sampling method: Regular.
Set resolution to: 0.05 degrees. This may be of your choice.
Click Create. Save as:
Testing_Dataset.gpkg.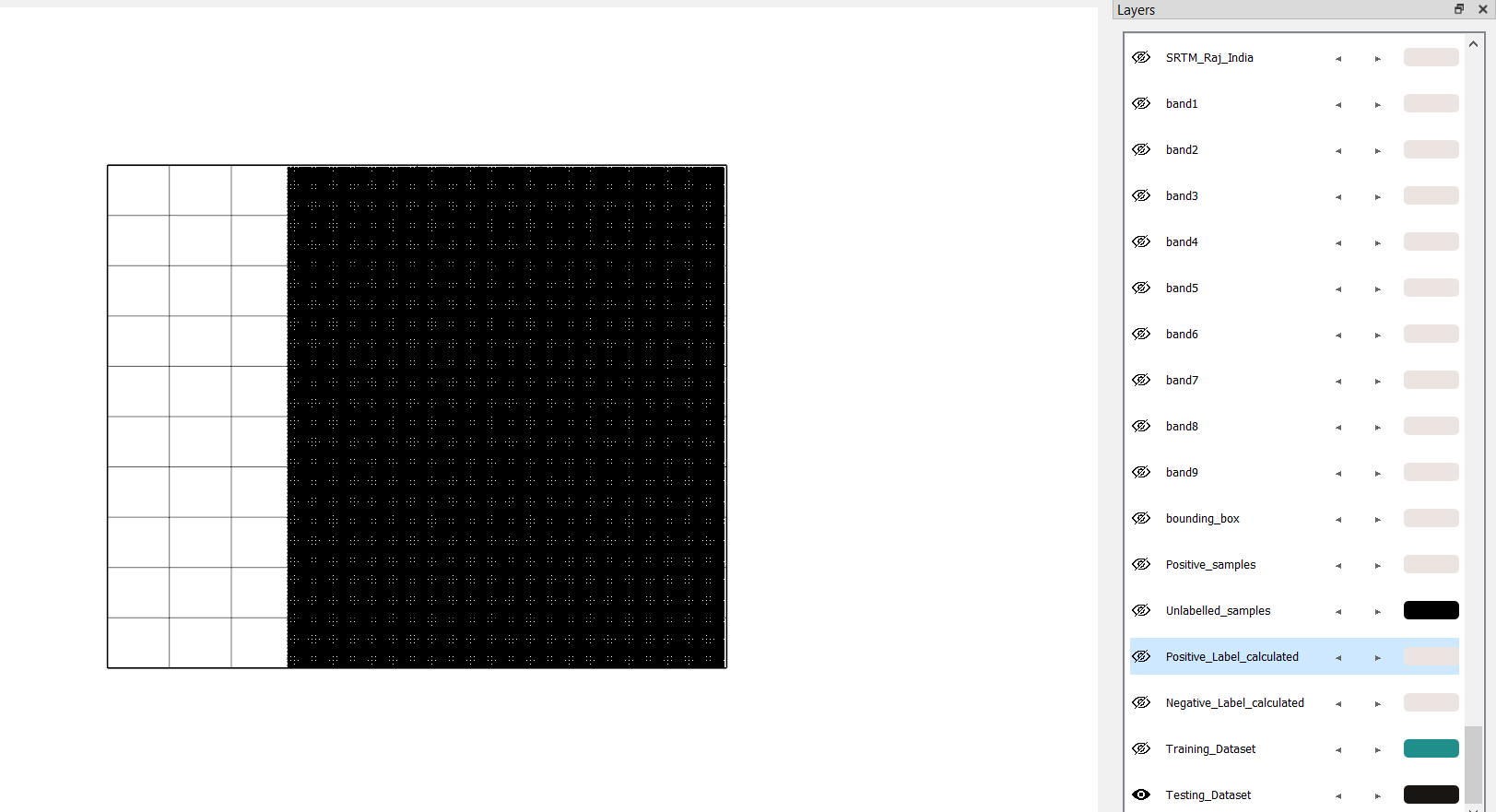
Prediction using Trained Model:
Navigate to Models → Supervised → PU Bagging.
Select Existing Model.
Select PU_Model.
Choose:
Testing_Dataset.gpkgas Data for Prediction.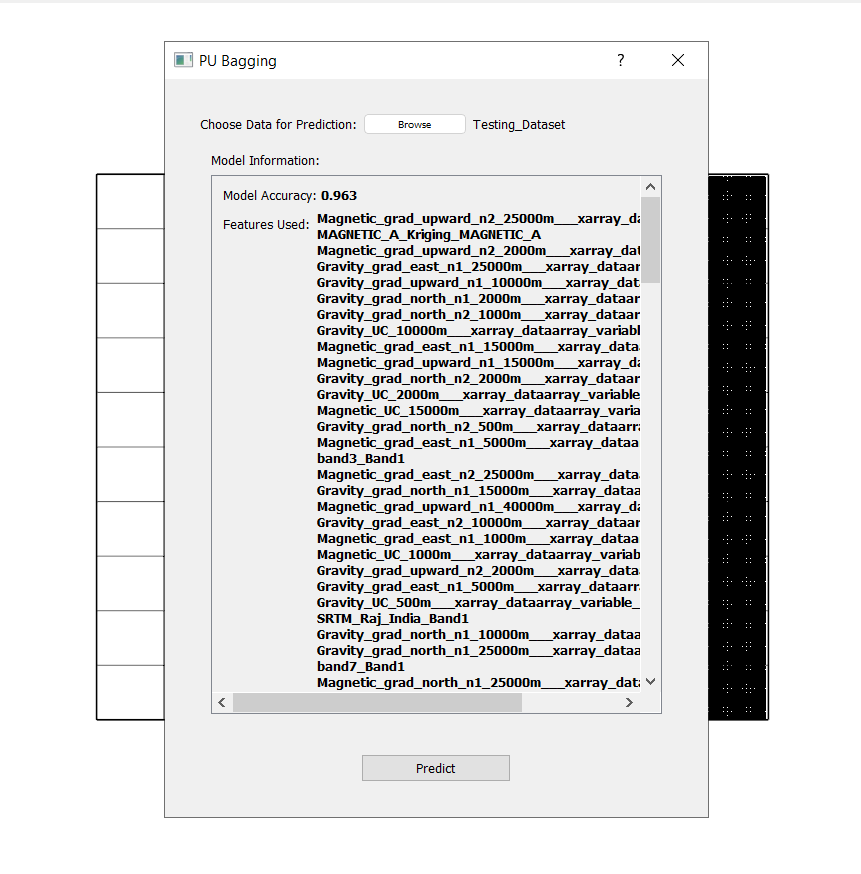
Click Predict
You now have your PU Bagging prediction.
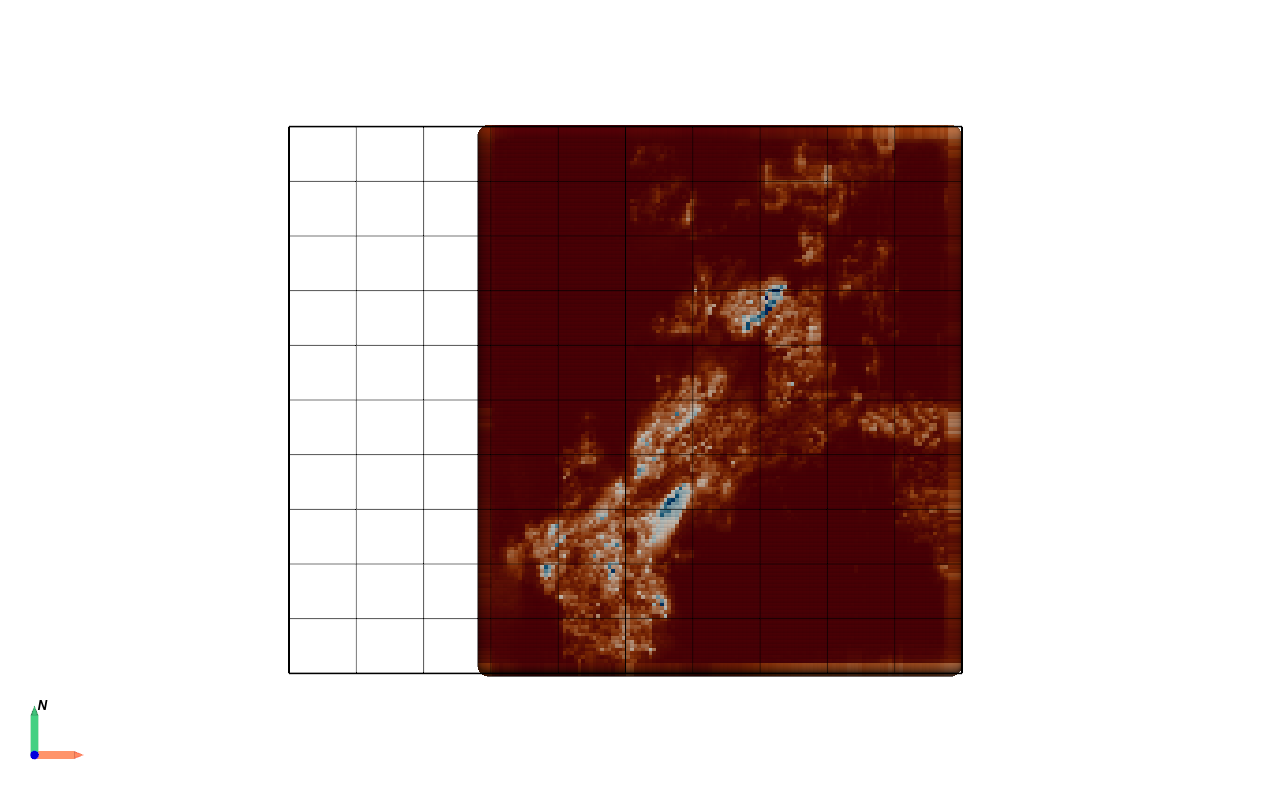
Visualizing Prospectivity Map:
Adjust colormap of your choice for better visualization and overlay the deposits layer to see how well the model has performed.